Harnessing the power of the sun to run your home might seem like science fiction, but it’s a practical and increasingly popular reality. Many homeowners are curious about making the switch but are stopped by a fundamental question: how does solar energy work, exactly? Understanding the process is the first step toward making a confident decision for your home and finances.
Table of Contents
This guide will demystify the technology behind residential solar. We’ll break down the simple science of how do solar panels work on a house, transforming pure sunlight into the usable electricity that powers your daily life. At RenewGenius, we believe that knowledge is power—both literally and figuratively—and our goal is to provide a clear, straightforward explanation.
The Core Component: The Photovoltaic (PV) Cell
Before we look at the whole system, let’s zoom in on the building block of every solar panel: the photovoltaic (PV) cell. These small cells are responsible for the magic of converting light into electricity.
What Are PV Cells Made Of?
Most PV cells are made from silicon, a semiconductor, arranged in two layers. One layer is treated to have a positive charge, and the other a negative charge, creating an electric field between them. Think of it like the positive and negative terminals on a standard battery.
The Photovoltaic Effect: Turning Sunlight into DC Electricity
This is the key to understanding how is solar energy converted into electricity. The process is called the photovoltaic effect.
- Sunlight is made of tiny packets of energy called photons.
- When these photons strike the silicon PV cell, they transfer their energy to electrons, knocking them loose from their atoms.
- The electric field within the cell pushes these free electrons to one side, creating an electrical current.
This current is known as Direct Current (DC) electricity. It’s the same type of power you find in batteries, but it’s not what most home appliances use. That brings us to the next step in the system.
Step-by-Step: How Solar Panels Work on a House
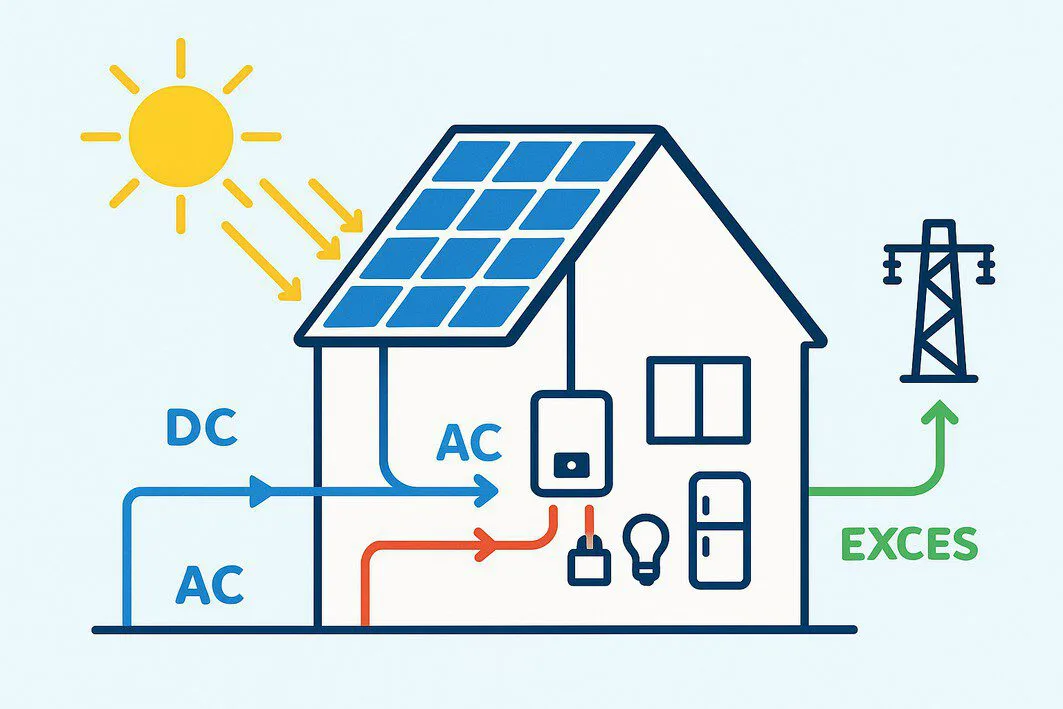
Now, let’s zoom back out and see how all the components work together in a typical residential solar installation.
Step 1: Sunlight Activates the Solar Panels
It all starts with the sun. Solar panels, typically mounted on your roof, are positioned to capture the maximum amount of sunlight throughout the day. Each panel contains dozens of the PV cells we just discussed.
Step 2: Panels Convert Sunlight to DC Electricity
As sunlight bathes the panels, the photovoltaic effect happens simultaneously across all the cells. The loose electrons begin to flow, generating a steady stream of DC electricity. This raw power is collected by the wiring in the panels and directed onward.
Step 3: The Inverter Converts DC to AC Electricity
The DC electricity from your panels flows to a crucial piece of equipment called an inverter. The inverter’s job is to convert the DC electricity into Alternating Current (AC) electricity. AC is the standard form of electricity used to power appliances, lights, and electronics in homes across the country.
Step 4: AC Electricity Powers Your Home
From the inverter, the usable AC electricity travels to your home’s electrical panel (or breaker box). From there, it’s distributed through your home’s wiring to your outlets and fixtures, powering everything just as electricity from the grid would. As long as the sun is shining, your home will automatically use the solar power first before drawing any from the utility company.
Step 5: Excess Energy and Net Metering
What happens on a very sunny day when your panels produce more electricity than your home is using? This excess power doesn’t go to waste. Instead, it’s sent back to the utility grid. Your utility company credits you for this power through a billing mechanism called “net metering”. This credit can then be used to offset the cost of any electricity you pull from the grid at night or on cloudy days.
What Happens When the Sun Isn’t Shining?
A common question is what happens at night or during heavy cloud cover. Your home doesn’t just shut down. You have two primary options:
- Relying on the Grid: In a standard grid-tied system, your home will seamlessly switch to drawing power from the utility grid when your panels aren’t producing. Thanks to the net metering credits you earned during the day, your bill will still be significantly lower.
- Solar Batteries: For greater energy independence, you can add a solar battery to your system. The battery stores the excess DC electricity your panels produce during the day. At night, your home can draw from this stored energy instead of the grid.
Making an Informed Decision with RenewGenius
Understanding how solar panels work is the foundation for appreciating their value. Now that you see the straightforward process of converting sunlight into savings, the next step is to understand what that means for you specifically.
As a resource focused on residential solar solutions, RenewGenius is dedicated to providing homeowners with a comprehensive solar knowledge base. We believe an informed decision is the best decision. Once you grasp the mechanics, it’s easier to explore the many solar energy benefits, which include:
- Significant cost savings
- A higher home value
- Energy independence
- A smaller carbon footprint
To see how these benefits translate into real numbers for your home, our ROI calculator can help you estimate your potential savings and payback period.
The technology is simple, elegant, and powerful. By converting sunlight into clean, renewable energy right on your rooftop, you take control of your power and invest in a more sustainable future.









