
Are you wondering which type of solar panel is best for your energy needs? Solar power has become increasingly popular in recent years as an eco-friendly way to provide electricity. With the growing demand, more and more types of solar panels are becoming available on the market. From flexible photovoltaic film to traditional rooftop arrays, there’s a perfect panel out there for everyone seeking sustainable energy sources.
This article provides an overview of the different types of solar panels that are currently available and what each one offers in terms of performance, efficiency, cost, and installation requirements. We’ll discuss the pros and cons associated with each type so you can make an informed decision about which will work best for you.
Finally, we’ll talk about how advances in technology have made it easier than ever before to install solar panels at home or at businesses without breaking the bank. So if you’re ready to take advantage of this clean source of energy, let’s dig into the various kinds of solar panels that can help fulfill all your renewable energy needs!
Solar panels come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they can be divided into three main categories: monocrystalline solar, polycrystalline solar, and thinfilm solar panels. Monocrystalline panels are composed of the purest silicon crystals and typically have a black hue. They’re also the most efficient type of panel available, making them popular among those looking to maximize their energy output on limited space. Polycrystalline panels use an alloy of multiple types of silicon crystals, resulting in a blue-hued product that’s slightly less efficient than monocrystalline models. Lastly, thinfilm solar panels are made with layers of photovoltaic material which is then mounted onto metal or glass backing. Although these panels tend to have lower efficiency ratings than the other two types mentioned above, they make up for it by being more cost-effective and easier to install due to their light weight and flexible design.
Now that we know about the various types of solar panels available let’s explore what type of solar panel is most commonly used?
It is widely recognized that the two primary types of solar panels are monocrystalline and polycrystalline. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, these particular technologies have been around for a number of years and account for most photovoltaic (PV) systems installed in the United States. The American Solar Energy Society also provides helpful information on this topic.
In terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness, monocrystalline solar panel technology has shown its superiority:
Ultimately, it’s clear that monocrystalline solar panels offer numerous benefits over their counterparts due to their superior efficiency and compact size—making them one of the best options for residential installations seeking reliable electricity generation at a reasonable price point. With advances in research and development continuing to drive innovation in renewable energies, there is no doubt that monocrystalline will remain the popular choice among homeowners looking to make the switch to clean energy sources.
This begs the question: what about the remaining four main types of solar panels?
To answer this query, we must explore not only their individual properties but also how they all fit together into a comprehensive PV system design.
Solar panels are made up of multiple solar cells, each of which contains a photovoltaic material that turns sunlight into energy. There are four main types of solar panel, all with their own unique characteristics. Let’s look at these in more detail.
The first type is the monocrystalline solar panel. These panels have the highest efficiency and longest life span, making them ideal for powering large systems like homes or businesses. As their name suggests, they contain single-crystal silicon wafers to create an efficient conversion rate from sun to electricity. They also perform well under standard test conditions (STC) due to their highly reflective surfaces.
The second type is polycrystalline solar panels. Unlike monocrystalline modules, this type uses multiple crystals that have been melted together to form square-shaped cells on the surface of the module. Although not as efficient as monocrystallines, they tend to be less expensive and require far less space than other types – making them great options for those looking to save money or fit many modules onto one rooftop.
Finally, bifacial solar panels are transparent on both sides and can absorb light from both above and below them – meaning they get twice as much exposure to sunlight as traditional models do! This makes them incredibly powerful when it comes to generating power but unfortunately there aren’t many commercially available yet so you’ll need to research carefully before investing in any products containing these new technologies.
These are the four main types of solar panel currently available – each offering its own advantages depending on your needs and budget constraints. Knowing what kind best fits your project is key to ensuring optimal results from your investment in renewable energy sources.

John and Mary were interested in installing solar panels to reduce their carbon footprint. After researching the market, they decided that monocrystalline solar panels would be the best choice for them. Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single silicon crystal and feature a sleek black surface with no visible gridlines. They possess higher efficiency than other types of solar panel technology due to their superior cell structure, making them the perfect option for John and Mary’s needs.
Monocrystalline solar panels have grown increasingly popular over recent years as more people become aware of their durability and compatibility with different mounting systems. Additionally, there is an increasing trend towards bifacial solar panels which benefit from double-sided exposure to sunlight, allowing them to generate more electricity than traditional models. This makes monocrystalline a great choice for those looking to maximize energy yields while still using aesthetically pleasing components on their roof or property.
The advantages offered by monocrystalline solar panels make them the preferred option among homeowners who want reliable performance and attractive designs at affordable prices – all factors that helped John and Mary decide on these powerful yet efficient products for their home project. As such, it’s clear why this type of technology has gained traction within the global solar panels market despite its high upfront cost.
With so many benefits available from choosing monocrystalline technology, what exactly are these innovative solutions made of?
Monocrystalline solar panels are made of a single-crystal silicon wafer. These wafers are cut from cylindrical ingots, which have been grown in a process called the Czochralski method. The cells used to make up these monocrystalline solar panels are typically constructed with cadmium telluride (CDTE) or amorphous silicon as well as crystalline silicon.
The main difference between monocrystalline and polycrystalline is that monocrystalline has higher efficiency ratings due to its higher purity levels. This is because purer materials absorb more light energy than impure ones do. Below is a table comparing the two types of solar panel:
| Monocrystalline | Polycrystalline |
|---|---|
| Higher Efficiency Rating | Lower Efficiency Rating |
| Pure Materials Absorb More Light Energy | Impure Materials Absorb Less Light Energy |
| Costlier than Polycrystallines | Cheaper than Monocrystallines |
It’s important to note that while monocrystalline solar panels tend to be more efficient, they also cost significantly more than their less efficient counterparts. However, if you want your renewable energy system to be as effective as possible it may be worth investing in them rather than opting for cheaper options like polycrystalline solar panels. Ultimately, the decision depends on what your needs and budget are so it’s best to weigh all the pros and cons before committing to one type over another. With this information in mind you can begin making an informed decision about which type of solar panel will work best for you and your home’s energy needs

Polycrystalline solar panels are a type of photovoltaic panel that is used in residential and commercial applications. These types of panels use multiple small crystallites to capture the sun’s rays, which then convert the light into electricity. While polycrystalline solar cells do not have as high efficiency ratings as monocrystalline cells, they tend to be cheaper and more widely available than their counterpart.
What separates polycrystalline from other solar cell materials is its ability to convert sunlight into energy at slightly lower temperatures compared to other technologies such as cadmium telluride (CDTe). This allows it to produce more electrical current when exposed to direct sunlight. Additionally, because of its low-temperature operation capability, this form of photovoltaics can operate even on partly cloudy days and still generate enough power for most needs.
Though polycrystalline has been around since the early 2000s, recent advancements in technology have allowed manufacturers to create higher efficiency modules with greater output per area or module size. This makes them an attractive choice for many homeowners looking for an efficient way to generate renewable energy without spending too much money upfront.
With these advantages in mind, let’s take a look at what these types of solar panels are made up of – what components make up a polycrystalline solar panel?

Polycrystalline solar panels are a popular choice among homeowners and businesses, as they offer an economical way to access renewable energy. These panels are composed of different materials that vary in efficiency and cost. Here’s a breakdown:
These components combine to form efficient yet affordable polycrystalline solar panels which work best when exposed to direct sunlight for extended periods throughout the day. By harnessing the sun’s power through these types of panels, people around the world have been able to take control of their own energy needs while reducing dependence on traditional sources like fossil fuels. With such versatility at hand, all that’s left now is finding out what kind of thin-film solar panel you need for your home or business!
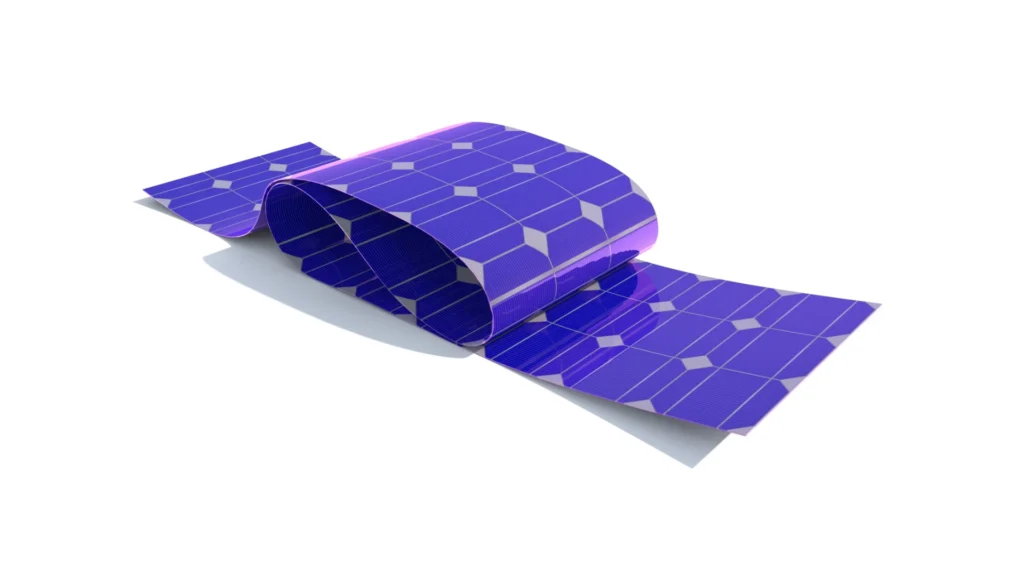
The next step in the journey of solar panel types is thin-film solar panels. Thin-film technology uses a variety of materials, including Cadmium Telluride (CDTE) or amorphous silicon (a-Si). These are deposited into ultra-thin layers onto glass or metal substrates to create photovoltaic cells. It’s an effective way to generate electricity from sunlight without needing large amounts of material like traditional crystalline silicon modules require.
Thin film solar panels take up less space than other types, making them ideal for rooftops that have limited area and installations where aesthetics are important. As they don’t need as much raw material as other module technologies, cost savings can be achieved through their manufacture too. They also offer more flexible installation options due to their lightweight nature and ability to bend around curves such as roof tiles and ridges.
One downside of thin film solar panels is that although they use less energy per watt generated, overall efficiency tends to be lower when compared with other forms of PV technology. This means you’ll likely need more square footage covered by these panels in order to achieve similar output levels from conventional alternatives – something which could affect your budget if you’re working within tight constraints.
Eagerly looking forward we turn our attention towards what are thin-film solar panels made of?
Thin-film solar panels are becoming increasingly popular, with up to a third of the global photovoltaic market share in 2018. Thin-film solar panels have their own set of advantages compared to traditional crystalline silicon models, but they also come with important considerations when it comes to material composition. The most common type of thin film is Cadmium Telluride (CdTe), which is made by mixing cadmium chloride and tellurium chloride together in an amorphous silico form. This combination creates more layers than other forms of thin film which increases the efficiency and power output of these cells.
Amorphous Silico is also known as ‘glass sandwich’ technology because two sheets of glass sandwich a layer of very thin silicone cell that has been deposited on top. When light passes through both sides of the panel, electricity is generated from the CdTe cell sandwiched between them. These thin films offer several distinct benefits over other types such as increased flexibility for installation purposes, improved temperature resistance and higher efficiency ratings at lower cost per watt since fewer materials are required for production. Additionally, due to its lightweight nature, less energy is consumed during shipping and handling making this option even more attractive for potential buyers looking for efficient yet cost effective solutions.
These properties make Thin Film Solar Panels ideal for many applications ranging from residential rooftops to large scale utility projects. Their versatility makes them suitable for challenging conditions while providing superior performance under varying weather conditions such as high temperatures or low sunlight exposure areas like remote regions or deserts where space might be limited. With so much to offer, it’s easy to see why Thin Film Solar Panel technology continues to gain popularity among commercial and residential customers alike who want reliable energy sources without breaking the bank.
In addition to the traditional photovoltaic cells, there are several other types of solar panels available today. With various advantages and disadvantages, each type has its own unique capabilities. Let’s take a look at some of these other solar panel types.
| Type of Solar Panel | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cadmium Telluride (CDTE) | High efficiency in low-light conditions Low cost production |
Toxic materials used in manufacturing Susceptible to overheating |
| Amorphous Silicon | Flexibility allows for curved surfaces Good performance at high temperatures |
Lower energy output than monocrystalline or polycrystalline panels |
Each type of solar cell offers different benefits depending on your needs. Cadmium telluride (CDTE) is one of the most efficient types out there, with an impressive ability to perform even in low light conditions. However, this comes at the expense of toxic materials being used during production. Amorphous silicon cells have their own set of advantages as well; they can be manufactured into flexible shapes and sizes, making them ideal for fitting onto oddly shaped surfaces such as cars or boats. On the downside, amorphous silicon is not as efficient compared to monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels when it comes to energy output.
Solar panel types come down to which ones best suit your individual needs and preferences – whether you’re looking for maximum efficiency or something more affordable and versatile. Understanding what works best for you can help make sure that you get the most out of your renewable energy system without breaking the bank! Now let’s move on to discuss how important solar panel efficiency really is.
Solar panels are a great way to generate renewable energy and reduce your dependence on conventional sources of power. But the efficiency of solar cells is key when it comes to deciding which type of panel you should use for your home or business.
There are three main types of solar cells: Amorphous Silicon (a-Si), Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) and Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS). Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, but all have one thing in common — they convert sunlight into electricity with varying degrees of efficiency.
Here’s a quick overview of the differences between these technologies:
Efficiency is an important factor when considering different types of solar cells as it can determine how much money you save from using them. For example, CdTE has the highest efficiency rating among the three options mentioned above at around 20%, while amorphous silicon lags behind at about 12%. As such, if you’re looking for maximum savings over time, then CDTE might be worth investing in despite its higher upfront costs.
Now that we’ve discussed various types of solar panels and their respective efficiencies, let’s take a look at what’s the lifespan of solar panels?
Solar panels have an incredible lifespan, especially when compared to other energy sources. The most common type of solar panel is the Cadmium Telluride (CDTE). This type of solar cell can last up to 30 years with minimal degradation in performance over time. Other types such as Polycrystalline Silicon and Monocrystalline Silicon are also known for their long lifespans and can last upwards of 20-25 years before needing replacement.
Due to advancements in technology, even newer forms of solar cells such as Thin Film Solar Cells have become increasingly popular due to their longer lifespans. These cells typically last around 10-15 years depending on proper maintenance and use, making them a great option for those looking for a more efficient solution.
Regardless of the type chosen, one thing remains true: investing in solar panels can be incredibly rewarding and beneficial for both individuals and businesses alike – not only do you get clean renewable energy but you’ll save money by avoiding costly repairs or replacements! How efficient are different types of solar panels?
The sun’s energy is a limitless resource, and harnessing it with solar panels can provide electricity for our homes and businesses. With the ever-growing demand for energy efficiency, understanding what type of panel will bring you the most bang for your buck is essential.
Cadmium telluride (CDTE) is one of the more efficient types of solar panels available on the market today, boasting an efficiency rate around 17%. This makes them ideal for those looking to maximize their savings while simultaneously reducing their carbon footprint. However, because they require special handling during installation due to toxicity concerns, many homeowners opt instead for amorphous silico cells that offer similar performance at a lower cost. These cells have an efficiency rating of 11%, which means they are not as effective when exposed to direct sunlight but still produce substantial amounts of power over time.
Regardless of which type you choose, all solar panels produce clean renewable energy and come with benefits such as minimal maintenance requirements and no need to purchase fuel like oil or natural gas. To help ensure that you select the right option for your needs, there are several factors that should be considered before making a decision about which type best suits your home or business’ needs.
Now that you know the different types of solar panels and their respective efficiency ratings, it’s time to consider what type of panel is best for your needs. Each type has its own unique characteristics that should be taken into account when selecting a panel type. Below is a table outlining some factors to consider when choosing between cadmium telluride (CdTe), amorphous silicon (a-Si) and other solar cells:
| Factors | Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) | Amorphous Silicon(A-Si) | Other Solar Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost per Watt | Lowest | Intermediate | Highest |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate | Low |
| Durability in extreme weather | Good | Fair | Poor |
| Ability to generate power at night | No | No | Yes |
The cost per watt of CdTe panels is the lowest compared to other types of solar panels. They are also more efficient than A-Si or other traditional solar cell technology, making them an ideal choice if you want maximum energy output from your system while keeping costs low. However, they may not be as durable in harsh climates due to their sensitivity to temperature fluctuations. On the other hand, A-Si panels are less expensive but still provide reasonable efficiency levels for most applications. Additionally, these panels are quite durable and have been known to perform well even in hot temperatures. Finally, although other types of solar cells such as polycrystalline or monocrystalline can produce higher efficiencies than both CdTe and A-Si, they tend to come with a much higher price tag and may require more maintenance over time.
When deciding on which panel type is right for your project, take all of these factors into consideration along with any local regulations governing installation requirements. By doing this research upfront, you will ensure that you select the most appropriate product for your home or business – one that provides optimal performance based on its individual specifications while providing long term value over time.
I. We can agree that solar panels are a great way to save money and make an impact on the environment. They provide reliable energy in all sorts of weather conditions, making them a smart investment for any homeowner. With government incentives available, it’s more affordable than ever before to install solar panels.
II. The sun is symbolic of hope and potential – when we invest in our own solar panel system, we’re investing in a brighter future not just for ourselves but for generations to come. It doesn’t take up much space either, so you don’t have to worry about your home or property being cluttered with equipment. Plus, they require very little maintenance once installed!
III. Installing solar panels is one of the most rewarding decisions I’ve made as a homeowner. Not only am I saving money every month on my electricity bill, but I’m also doing something good for the planet and setting an example for others around me. Investing in this renewable source of energy has been life-changing for me – hopefully it will be for you too!
Installing solar panels can be an exciting way to save money. It is like a beacon of freedom, allowing you to take control over your finances and break away from dependence on traditional energy sources. Whether you’re looking for long-term savings or just want the satisfaction of helping the environment, going solar has many benefits that are worth considering.
The amount of money saved by installing solar panels depends entirely on how much energy is produced with them. Solar panel systems come in several sizes and types, ranging from large rooftop installations to small portable devices that generate power when exposed to direct sunlight. Depending on where you live, some areas may even offer incentives such as tax credits or rebates which can help reduce the cost significantly. In addition, depending on the type of system chosen, there will be different maintenance fees associated with it as well.
So what kind of financial return can you expect? On average homeowners who install solar panels see around 15-20% annual returns on their investments. This number varies greatly depending on factors like location, size of installation, and type of system used; however, most people find that they are able to pay off their investment within 5 years due to lower electricity bills and other savings methods offered through solar technology. Overall many people find that investing in a quality solar solution makes good economic sense — both now and in the future!
The advantages of solar panels are undeniable. But for many, reliability and performance in different weather conditions are a concern. Are solar panels reliable in varying weather? The answer is yes! Solar panels can perform reliably even when the environment around them changes.
Solar energy systems use photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electrical current. These cells continue to work regardless of rain or snowfall, as long as there’s still daylight available. In fact, some studies show that solar panel efficiency actually increases with lower temperatures due to reduced heat and air resistance within the cell’s structure. And don’t worry about cloudy days; most solar energy systems are designed to store excess energy during sunny periods so they can draw upon it on those overcast days.
Not only do solar panels remain functional under changing weather patterns but they also offer other benefits like being low maintenance and eco-friendly – two qualities that make them an attractive option for homeowners looking for sustainable sources of power. Additionally, if you live in an area where net metering laws exist, then every kWh generated from your solar array will be credited back towards your electric bill – meaning more money saved in the long run! It’s clear why people choose this type of renewable energy — not just because it’s efficient and dependable, but also because its rewards go beyond just financial gain.
As people become more aware of the benefits of renewable energy, they may be curious to find out if there are any government incentives for installing solar panels. Fortunately, yes! The good news is that in many countries around the world, governments have implemented various financial incentives and rebates to encourage citizens to install solar panels on their homes or businesses.
These incentives often come in the form of tax credits, grants, or subsidies, which can drastically reduce the cost of installation for those looking to make a switch from traditional energy sources such as fossil fuels. In addition, some governments also offer net-metering systems that allow homeowners to sell electricity back into the grid at a higher rate than what they pay for it – essentially turning your home into an income generator while helping save our planet too!
The possibilities are truly endless when it comes to harnessing the power of solar energy and with so many generous government programs available today, now might just be the perfect time to take advantage of this clean and limitless source of energy – unleashing yourself from expensive bills forever!
Installing solar panels is an excellent way to reduce your dependence on the utility grid and do your part for environmental conservation. But how much space do you need to install these energy-saving systems? This will depend on the type of panel you choose, as well as its size and power output.
As with any home improvement project, it’s important that you consider all aspects before diving in. You’ll want to determine what kind of system works best for you, based on factors like cost, efficiency, and location. For instance, if you live in a sunny area with lots of open space available then larger photovoltaic (PV) panels could be ideal. On the other hand, smaller rooftop or ground mounted systems may work better in urban areas with limited roof space.
No matter which option you go with, there are plenty of ways to maximize the use of your space while getting maximum benefit from the installation. Mounting options can include tilt frames, flat racks or even ballasted systems – all designed to make efficient use of whatever surface area is available. And don’t forget about government incentives; many countries offer tax credits and rebates for those who invest in renewable energy sources such as solar PV systems.
Making a smart decision when investing in solar technology doesn’t have to be hard. With careful planning and consideration for both short-term needs and long-term goals, anyone can enjoy the benefits of clean energy without sacrificing valuable real estate!
Maintaining solar panels is not as difficult as it may seem. To put it in a nutshell, the upkeep of such systems is minimal and easy to handle. With that being said, there are still certain steps one must take in order to ensure they’re getting the most out of their investment.
To start off with, you need to be aware that any system needs regular cleaning and maintenance, no matter the size or complexity. This means taking some time each year, or even more often if necessary, to inspect your system for any damage or debris buildup on its components. You should also look into having an expert come over once every few years for a thorough inspection to make sure everything is running optimally.
When it comes down to it, installing solar panels doesn’t have to feel like a daunting task – as long as you stay ahead of potential issues by regularly checking up on them. Taking the time to do so will save you from costly repairs down the road and help keep your energy bills low while powering your home with clean renewable energy sources. As an added bonus, this small effort can bring about big peace-of-mind knowing your investments are properly cared for and working at peak efficiency!

What Is The Expected Lifespan Of Batteries In A Residential Solar System? Share: Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Residential solar systems have become popular as more

Difference Between String And Microinverters In A Solar Panel System? Share: Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest The world is gradually shifting towards renewable energy sources, with

How Do I Choose The Right Solar Panel Manufacturer? Share: Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest As the world becomes more environmentally conscious, many individuals are turning

How Do I Choose The Right Inverter For My Solar Panels System? Share: Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Choosing the right inverter for your solar panel

What Kind Of Backup Power Options Are Available With A Solar Panel System? Share: Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Solar panel systems have become increasingly popular

What Is The Expected Lifespan Of A Solar Inverter? Share: Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Pinterest Solar energy is becoming increasingly popular as a source of renewable