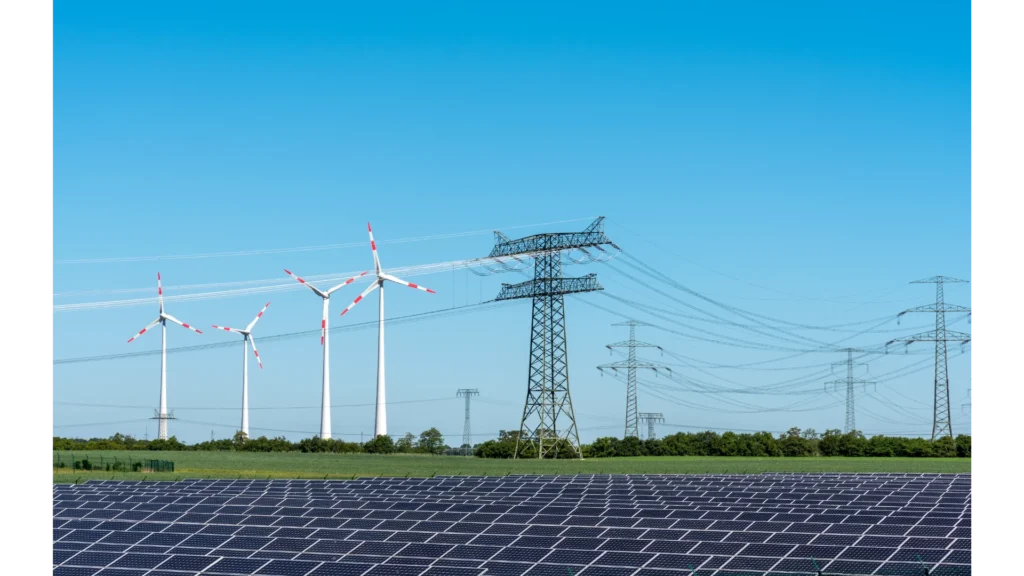

As more and more individuals turn to renewable energy sources, the question arises as to whether or not it is possible to still use electricity from the grid if one has installed solar panels.
The answer is yes, it is possible to supplement solar energy with grid electricity, and in fact, this combination can provide a reliable source of power that meets the needs of many households.
Solar panels generate electricity by converting sunlight into usable energy. While this technology has come a long way in recent years and can now provide sufficient power for many households, there may be times when additional electricity is needed.
This is where the grid comes in. By connecting their solar panels to the electrical grid through what is known as net metering, homeowners can draw on the power provided by their local utility company when their solar panel system isn’t producing enough energy. In this way, they can enjoy both the benefits of renewable energy and reliable access to traditional electricity sources when needed.
Understanding the interaction between solar panels and the electrical grid is crucial in comprehending how these technologies can complement each other.
When a solar panel system generates more electricity than it requires, the excess energy flows back into the grid. On the other hand, when there is insufficient power from solar panels to meet demand, electricity from the grid kicks in to make up for any shortfall.
This arrangement has several benefits for homeowners. Firstly, they can offset their energy bills by harnessing extra electricity from sunlight during peak hours of sunshine. Secondly, they can sell enough electricity to the electric utility through net metering programs and earn credits or cash payments. Thirdly, homes with solar panels remain connected to the grid and have access to reliable power, even on cloudy days or at night, thanks to the battery.
However, there are also challenges associated with using solar panels and clean energy in tandem with traditional sources of electricity and battery storage. For instance, electricity grids were not designed to handle two-way power flows created by distributed generation systems like rooftop solar arrays or small wind turbines, which can meet the growing energy needs and provide energy storage.
As such, utility companies must upgrade their infrastructure and regulatory frameworks to integrate renewable energy sources seamlessly into existing grids without compromising reliability or safety standards.
In summary, while using electricity from a home’s solar panel system and the electrical grid simultaneously is possible, this requires careful planning and coordination between homeowners and utility providers.
By working together towards a common goal of reducing carbon emissions while ensuring stable energy supplies for all consumers, we can achieve a cleaner future powered by renewable resources like the smart grid, electricity grid, electric grid, and solar provider.
Implementing net metering policies allows individuals with solar panels to sell excess energy back to the grid, incentivizing the adoption of renewable energy sources.
Net metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar panel owners for any excess electricity they generate and sends back to the grid. This surplus can be used during cloudy or nighttime periods when solar panels aren’t generating enough power.
Net metering has several benefits. It encourages people to install solar panels and produce their own electricity, reducing dependence on fossil fuels while promoting clean, renewable energy sources.
Additionally, it helps reduce peak demand for electricity when most people use high levels of power, such as hot summer afternoons or cold winter evenings. By encouraging distributed energy generation through the use of solar arrays and solar batteries, net metering also strengthens local grids and reduces transmission losses from transmitting electricity over long distances. This is especially beneficial for utilities.
In conclusion, understanding the net metering system is crucial for anyone considering installing solar panels in their home or business. It provides a means of reducing carbon emissions and saving money on utility bills by selling excess electricity to the grid. As more homeowners choose this option for clean energy production, we can expect a significant reduction in our reliance on fossil fuels and increased use of renewable sources like solar power.
An effective strategy for maximizing the benefits of solar energy is to supplement it with grid electricity from the utility during periods of low sunlight availability. This approach ensures that households or businesses have a reliable source of electricity from the system at all times, regardless of weather conditions. Moreover, it allows surplus energy generated by solar panels to be fed back into the grid, which can earn credits through net metering and ultimately reduce overall electricity costs.
While using solely solar power may seem ideal in terms of environmental sustainability, there are certain limitations to this system. For instance, weather patterns such as cloud cover or rain can significantly impact the amount of electricity solar panels produce. During these times, supplementing with grid electricity becomes necessary to maintain sufficient power levels. Additionally, households or businesses that consume more energy than their panels produce will benefit from using grid electricity as a backup source.
Supplementing solar energy with grid electricity has become increasingly popular due to technological advancements and government incentives to promote renewable energy usage. However, it is important for consumers to carefully assess their specific needs before making any decisions regarding their energy consumption habits.
By taking advantage of both the smart grid and solar energy system, individuals can achieve greater freedom and control over their power usage while simultaneously reducing their carbon footprint. Adding solar batteries to the equation can further enhance the benefits of this solar energy world.
With the ability to seamlessly switch between solar and grid power, individuals gain more flexibility in managing their household or business’s daily operations with a reliable system.
The cost savings associated with utilizing surplus solar-generated energy through net metering incentivize consumers to invest in renewable sources such as solar panels for the electric grid, electricity grid, smart grid, and power grid.
The combination of a solar energy system and solar battery offers peace of mind when unexpected weather changes occur. With a tied solar setup, you can rely on clean and reliable power from the solar energy world.
Supplementing solar-generated energy with grid power eliminates concerns about running out of battery backup during extended periods without sunlight.
Investing in solar panels offers a promising opportunity for long-term cost savings and environmental sustainability, providing an appealing solution to rising energy costs and concerns over climate change. While the initial installation cost of solar panels may seem expensive, the long-term benefits are undeniable. Solar panels can generate electricity for 25-30 years with minimal maintenance costs, so homeowners can significantly reduce their reliance on grid electricity and save money on their monthly electric bills.
One way to illustrate the potential cost savings of solar panels is through a comparison table. The table below shows a household’s estimated annual electricity bill using only grid electricity versus grid and solar power. As you can see from the table, households that use solar power in conjunction with grid electricity can significantly reduce their annual energy bills.
| Households Using Only Grid Electricity | Households Using Both Grid Electricity and Solar Power | |
| Estimated Annual Bill | $1,500 | $700 |
Moreover, installing solar panels reduces reliance on traditional energy sources and adds value to your property. Studies have shown that homes equipped with solar panels sell faster than those without them because they offer an attractive feature to potential buyers looking to save money on energy costs. In fact, according to EnergySage’s Solar Marketplace Intel Report, homes equipped with solar panels sell faster than those without them by an average of 17%. Therefore, solar panel investment offers a win-win solution: reducing monthly expenses while increasing property values.
By investing in solar panels, homeowners can reap numerous benefits such as cost savings, environmental sustainability, increased property value, and attraction. Additionally, households that use grid and solar power have been known to enjoy significant reductions in annual energy bills compared to households relying solely on grid electricity. Furthermore, it’s interesting how this renewable energy source can increase the value and attractiveness of the property to potential buyers. In essence, investing in solar panels is an investment that keeps giving back over a long period.
Solar energy offers numerous environmental benefits, making it a compelling alternative to traditional energy sources. Here are three reasons why:
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: One of the most significant benefits of solar power is its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When fossil fuels are burned to produce electricity, they release carbon dioxide and other harmful gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. In contrast, solar panels produce clean, renewable energy without emitting harmful pollutants.
Another benefit of solar power is its ability to conserve water resources. Traditional power plants consume large amounts of water for cooling, which can strain local water supplies and harm aquatic ecosystems. Solar panels require little or no water to generate electricity, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to grid-powered plants.
Preserving Natural Habitats: The construction and operation of traditional power plants can devastate natural habitats and wildlife populations by disrupting ecosystems and polluting air and waterways. Solar panels have a much smaller environmental footprint than traditional power plants, making them a more sustainable for preserving natural habitats and integrating them into the grid.
By harnessing the sun’s power, we can significantly reduce our dependence on fossil fuels while promoting a cleaner, healthier environment for future generations.
In conclusion, solar panels can work with the grid to provide reliable and cost-effective energy for homes and businesses.
With net metering, excess energy generated by solar panels during peak sunlight hours can be sent back to the grid for credit, which can then be used when the solar panels are not producing enough energy.
This allows homeowners to supplement their solar power with grid electricity as needed.
In addition to cost savings, using solar panels also has environmental benefits, such as reducing carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels. Solar panels help to contribute to a more sustainable energy grid.
As technology advances, we can expect even more efficient and affordable options for incorporating renewable energy into our daily lives.
Overall, utilizing solar power and traditional electricity from the grid can help us move towards a more sustainable future.
When solar panels do not produce enough energy, individuals may still need to rely on electricity from the grid.
This is because solar panels do not always produce a reliable or consistent amount of energy, particularly in areas with less sunlight or during times of low activity.
Additionally, consumers may require more energy than their solar panels can provide at any given time.
In these cases, the use of traditional grid electricity can help supplement a household’s power needs and ensure that they have access to sufficient electricity at all times.
When solar panels produce more energy than is being used, the excess energy can be sent back to the grid through a process called net metering.
This allows homeowners with solar panels to receive credits on their utility bills for the excess energy they generate. These credits can then be applied towards future electricity usage when their solar panels are not producing enough energy.
Additionally, some utility companies may offer buyback programs where they purchase excess energy from homeowners with solar panels at a fixed rate.
This allows homeowners to earn additional income while reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to a more sustainable future.
The time it takes for solar panels to start generating savings largely depends on several factors, such as the cost of electricity, the size of the solar system, and how much energy is consumed.
Typically, residential solar panel systems achieve savings within five to seven years, with larger systems achieving savings in less time.
However, there are variables that can affect this timeline, such as fluctuations in energy usage and changes in electricity rates.
Additionally, regular maintenance and cleaning of the panels can help ensure optimal performance and extend their lifespan.
While initial costs may be high, investing in a solar panel system can provide long-term financial benefits while also reducing carbon footprint.
Connecting solar panels to the grid may entail some additional costs, such as installation fees and metering charges. These expenses vary depending on the location and size of the system, as well as local regulations and utility policies.
For example, some utilities require a special meter to measure incoming and outgoing solar panels’ power. In contrast, others offer net-metering programs that credit homeowners for excess electricity produced by their systems. Additionally, fees or taxes may be associated with connecting to the grid or maintaining a connection agreement with the utility company.
It is important to research these potential costs before investing in a solar panel system to ensure that it is financially feasible and sustainable in the long run.
The integration of solar panels on residential properties has become increasingly popular in recent years due to the potential energy savings and environmental benefits.
While there are clear advantages to utilizing this renewable source of energy, homeowners may be concerned about how it affects their home’s resale value.
Studies have shown that homes with solar panels tend to sell for more than those without, as they provide the added benefit of reduced energy costs.
However, the exact amount of added value varies depending on factors such as location, size and age of the system, and overall demand for solar-powered homes in the area.
Despite these considerations, investing in solar panels can be a wise financial decision for homeowners seeking a sustainable lifestyle while also potentially increasing their property’s market appeal.

How To Know If My Solar Compatible With Electrical Setup? Installing a solar panel system is an excellent way to reduce reliance on traditional electricity
How Do I Ensure That My Solar Panel System Is Properly Grounded? Properly grounding a solar panel system is crucial to ensure safety, optimize performance,

Can I Use My Ev’s Battery To Store Excess Solar Energy? The utilization of renewable energy sources such as solar power is on the rise,

Can I Monitor The Performance Of My Solar Panel System Remotely? Solar energy is becoming an increasingly popular alternative to traditional sources of electricity. With

What Is The Difference Between Solar And Photovoltaic? Solar energy is a topic that has been gaining more attention in recent years as people become

Can I Use Solar Panels To Power My Electric Vehicle? Can I use Solar Panels To Power My Electric Vehicle? The rise of electric vehicles