Considering a switch to solar energy is an exciting step toward energy independence and lower utility bills. But before enjoying the benefits, it’s crucial to understand the system itself. What are the major components of a solar system installed on your property? Knowing each part’s function helps you make a confident, informed decision.
Table of Contents
- What Are the Main Components of a Solar Panel System?
- Core Solar System Components Explained
- Essential Balance of System (BOS) Components
- Monitoring and Performance Tracking
- How Do All These Solar Parts Work Together?
- Choosing the Right Components for Your Home
- Your Complete Solar System Components List: A Final Checklist
This guide provides a complete solar system components list, breaking down every essential piece of hardware. We’ll explore the main components of a solar panel system and the supporting parts that make it all work seamlessly. As experts focused on residential solar solutions, our goal is to leverage our comprehensive solar knowledge base to empower you on your solar journey.
What Are the Main Components of a Solar Panel System?
At its core, a residential solar energy system is a collection of high-tech parts working in unison to convert sunlight into usable electricity for your home. While there are many smaller pieces, the system revolves around four primary components:
- Solar Panels (The Power Generators)
- Solar Inverter (The Power Converter)
- Racking and Mounting (The Foundation)
- Solar Battery (The Energy Reserve – often optional but increasingly popular)
Let’s dive deeper into these core parts and the other essential parts of a house solar system.
Core Solar System Components Explained
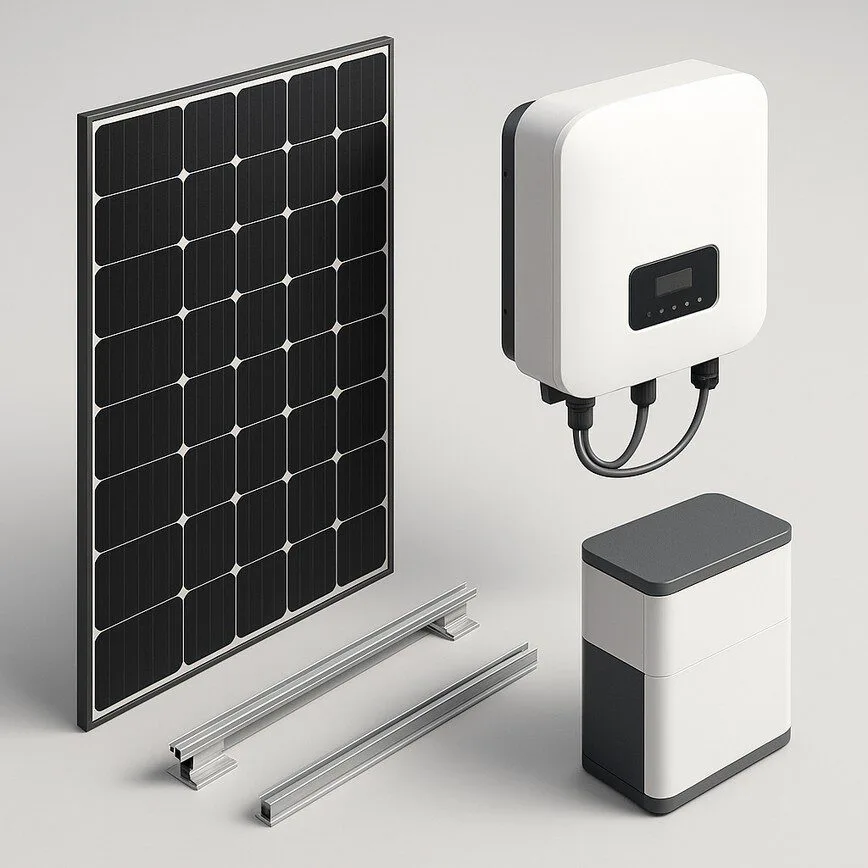

These are the heavy lifters of your system, responsible for the primary tasks of capturing, converting, and securing solar energy.
1. Solar Panels (Photovoltaic Modules)
This is the most visible component and what everyone thinks of first. Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells that absorb sunlight and, through a process called the photovoltaic effect, generate direct current (DC) electricity.
- How They Work: When sunlight photons strike the silicon cells in the panel, they knock electrons loose, creating an electric current.
- Common Types:
- Monocrystalline: Made from a single silicon crystal, these are highly efficient and have a sleek, black appearance. They are often the premium choice.
- Polycrystalline: Made from melted silicon fragments, these are slightly less efficient but more budget-friendly. They typically have a blue, speckled look.
- Thin-Film: A newer technology that is flexible and lightweight, but generally less efficient than crystalline options, requiring more surface area.
2. Solar Inverter
The electricity your solar panels generate is DC, but your home’s appliances and the utility grid run on alternating current (AC). The solar inverter is the brain of the operation, responsible for this critical conversion. It’s the brain of the operation.
- How It Works: The inverter takes the DC electricity from the panels and safely converts it into appliance-ready AC electricity.
- Common Types:
- String Inverters: A single, central inverter connects a series (or “string”) of panels. This is a cost-effective and reliable standard.
- Microinverters: A small inverter is installed on the back of each individual panel. This maximizes output, as the poor performance of one shaded panel won’t affect the others.
- Power Optimizers: A hybrid solution that pairs a central string inverter with optimizers on each panel to mitigate shading issues without the cost of a full microinverter setup.
3. Racking and Mounting System
The racking is the unsung hero of your solar installation. This framework securely fastens your solar panels to your roof or the ground. Its job is to withstand wind, rain, snow, and whatever else nature throws at it for decades.
- How It Works: Racking systems are engineered to attach to your roof’s rafters or a ground-based foundation, creating a secure and durable platform for the panels.
- Common Types:
- Roof-Mounted: The most common option for residential homes, it uses the existing roof structure to save space.
- Ground-Mounted: Ideal for properties with large, open spaces or roofs that are not suitable for installation. They can be optimally angled for maximum sun exposure.
4. Solar Battery Storage
A solar battery allows you to store the excess energy your panels generate during the day instead of sending it all back to the grid. This stored energy can be used at night, during power outages, or during peak-rate hours from your utility company.
- How It Works: The battery stores the DC electricity from your panels. When needed, that energy is dispatched to your inverter (or has its own inverter) to be converted to AC power for your home.
- Key Benefit: A battery provides true energy independence and resilience, ensuring you have power even when the sun isn’t shining or the grid is down.
Essential Balance of System (BOS) Components
Beyond the big four, several other parts of a house solar system are critical for safety, efficiency, and functionality. These are collectively known as the Balance of System (BOS).
5. Charge Controller
If your system includes a battery, a charge controller is essential. It acts as a regulator, managing the flow of electricity from the panels to the battery to prevent overcharging and extend the battery’s lifespan.
6. Wiring and Circuitry
Specialized, UV-resistant wiring connects all the components, from the panels to the inverter and into your home’s main electrical panel. Proper wiring is paramount for the safety, efficiency, and longevity of the entire system.
7. Disconnect Switches
Safety is non-negotiable. Disconnect switches are installed at key points in the system to allow for the flow of electricity to be shut off quickly. This is crucial for maintenance, repairs, or in case of an emergency.
Monitoring and Performance Tracking
How do you know if your system is working correctly? Modern solar setups come with sophisticated monitoring tools.
8. Solar Monitoring System
Usually accessed via a smartphone app or web portal, a monitoring system tracks your system’s real-time energy production, consumption, and battery status. It helps you visualize your savings and can automatically alert you or your installer if a problem is detected, ensuring you get the most out of your investment.
How Do All These Solar Parts Work Together?
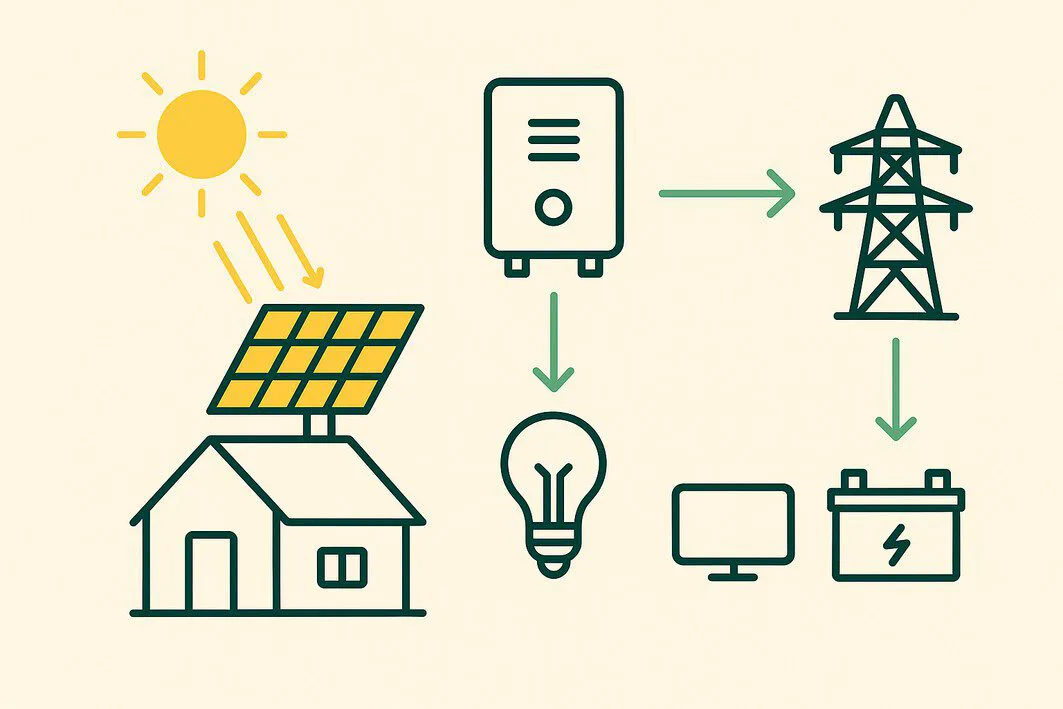
- Capture: Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity.
- Optimize (Optional): If installed, power optimizers condition the DC electricity before sending it to the inverter.
- Convert: The inverter converts the DC electricity into AC electricity suitable for your home.
- Power: The AC electricity flows to your home’s electrical panel to power your lights and appliances.
- Store (Optional): Excess electricity is used to charge your solar battery for later use.
- Export: Any remaining electricity not used by your home or stored in the battery is sent back to the utility grid, often earning you credits on your bill.
Choosing the Right Components for Your Home
Understanding this solar system components list is the first step. The next is choosing the right combination of products for your specific energy needs, roof type, and budget. Making an informed decision is key to maximizing your return on investment. This is where leveraging a comprehensive solar knowledge base becomes invaluable. By understanding the options, you can better evaluate quotes and system designs.
To take your decision-making to the next level, you can use our ROI calculator to estimate potential savings based on different system configurations. As you weigh your options, you’ll want to learn more about the specific models and types of panels, inverters, and batteries. To help with that, you can explore our in-depth guides on essential solar components.
Your Complete Solar System Components List: A Final Checklist
Here is a quick summary of all the parts of a typical residential solar system:
- Core Components:
- [ ] Solar Panels (PV Modules)
- [ ] Solar Inverter (String, Micro, or with Optimizers)
- [ ] Racking & Mounting System
- [ ] Solar Battery Storage (Optional)
- Balance of System (BOS):
- [ ] Charge Controller (for battery systems)
- [ ] Wiring & Fuses
- [ ] AC/DC Disconnect Switches
- Monitoring:
- [ ] Performance Monitoring System (App/Portal)
With this complete guide, you are now equipped with the foundational knowledge to confidently navigate conversations with installers and choose a system that will serve you well for years to come.









